![]() Statistics
Measurements
Statistics
Measurements
The Statistics Measurement functions are used to compute statistical estimators for the data in Image Windows and Plot Windows. For images, the data sample may include the entire image or be limited to a rectangular region. For plots, all plot series are used. The statistical estimator and parameters are selected from the Statistics Properties dialog and may range from a basic quantity like the Mean to a more complex computation such as SigmaClip or Skewness. For Image Windows, the Statistics Properties dialog provides the option to save the statistics results to the image header; however, the image must be saved to a file to permanently save the updated header.
To make a Statistics measurement, bring the Image Window or Plot Window to the top of the window stack.
For Image Windows, you can use the Image Cursor to define the measurement region.
For Image Windows, click the ![]() button on the main Measurements Toolbar
or use the Measure > Statistics command from the Image
Window menu.
button on the main Measurements Toolbar
or use the Measure > Statistics command from the Image
Window menu.
For Plot Windows, click the ![]() button
on the Plot Bar or use
the Measure > Statistics command from the Plot
Window menu. Statistical estimators listed in the
Statistics pane may be selected and marked in the plot
window; see Mark
Statistic.
button
on the Plot Bar or use
the Measure > Statistics command from the Plot
Window menu. Statistical estimators listed in the
Statistics pane may be selected and marked in the plot
window; see Mark
Statistic.
For Image Windows displaying an Image Set, the Image Cursor defines the same pixel region for all images, thus using an identical region of each image without re-positioning the cursor. Image Windows also provide the 'S' keystroke shortcut. See the Image Keys Pane.
The statistics in the following table can be selected for measurement using the Statistics Properties dialog. When the result is saved to the FITS header, the measurement region is added using the S_REGION keyword and the estimator and standard deviation are added using keyword names coded to fit into the 8-character length of a FITS keyword. If a given keyword already exists in the header, its value is updated with the new statistic. For further information, see "Saving Statistics to the FITS Header" under the Statistics Properties topic. To remove all statistics keywords from the FITS header, use the menu command Measure > Statistics Properties > Remove Statistics Keywords. The statistics measurements may be listed using the List Statistics Keywords command.
|
Properties of the Statistics Properties dialog |
|
|
Mean |
Calculates the simple average with no weighting or rejection of bad values. |
|
Mean - Geometric |
Calculates the geometric mean, which is a mean value weighted by the reciprocal of the individual values. |
|
Mean - Contra Harmonic |
Calculates the weighted harmonic mean value in which each weight involves the value raised to the p power. |
|
Mean - Yp Power |
Calculates the weighted mean value in which the weight is given by the exponent "p", which is the value raised to the p power. |
|
Mean - Alpha Clipped |
Calculates a clipped mean in which a specified number N(high) and N(low) values are excluded from the sample. |
|
Mean - Rank Clipped |
Calculates a clipped mean in which the specified percentiles %(high) and %(low) of values are excluded from the sample. |
|
Mean - Sigma Clipped |
Calculates a clipped mean in which values are rejected if more deviant than ß(high) and ß(low) above and below the sample distribution mean. Refinement of the calculated mean value is repeated up to specified maximum number of cycles. Use this method when calculating the mean value in the presence of deviant values that are outliers from a Normal distribution. |
|
Mean - MTM Sigma Clipped |
Calculates a clipped mean in which values are rejected if more deviant than ß(high) and ß(low) above and below the sample distribution estimator. This computation includes both the mean and median values of the sample distribution. Refinement of the calculated mean value is repeated up to specified maximum number of cycles. Use this method when calculating the mean value in the presence of deviant values that are outliers from a Normal distribution. |
|
Mid Point |
Calculates the midpoint between the sample minimum and maximum values. |
|
Median |
Calculates the sample median (50th percentile). |
|
Minimum |
Calculates the minimum values of the sample. |
|
Maximum |
Calculates the maximum values of the sample. |
|
Rank Percentile |
Calculates the ranked percentile value based on the %Rank parameter. For example, if %rank = 50, then the 50th percentile, or median, value is returned. |
|
Standard Deviation |
Calculates the Standard Deviation about the mean value. To calculate the standard deviation about a specified value, check the Reference Mean box and enter the target value. Otherwise, the ordinary standard deviation is calculated. |
|
Standard Deviation - Clipped |
Calculates the Standard Deviation in which values are rejected if more deviant than ß(high) and ß(low) above and below the sample distribution mean. Refinement of the calculated mean value is repeated up to specified maximum number of cycles. Use this method when calculating the standard deviation in the presence of deviant values that are outliers from a Normal distribution. |
|
Std Err of the Mean |
Calculates the Standard Error of the Mean. This is the standard deviation divided by the square root of the number of points in the sample, also known as the "error of the mean." This statistic is used when comparing the mean values for two different populations, such as the mean value of one image to the mean value of another image. Comparatively, the standard deviation measures the variation (or "scatter") of the sample values (e.g., pixels) with respect to their own mean. |
|
Std Err of the Mean - Clipped |
Calculates the Standard Error of the Mean in which values are rejected if more deviant than ß(high) and ß(low) above and below the sample distribution mean. Refinement of the calculated mean value is repeated up to specified maximum number of cycles. Use this method when calculating the standard deviation in the presence of deviant values that are outliers from a Normal distribution. This is the standard deviation divided by the square root of the number of points in the sample, also known as the "error of the mean." This statistic is used when comparing the mean values for two different populations, such as the mean value of one image to the mean value of another image. Comparatively, the standard deviation measures the variation (or "scatter") of the sample values (e.g., pixels) with respect to their own mean. |
|
Skewness |
Calculates the statistical skewness to characterize the symmetry of the sample distribution. A skewness value of 0 describes a symmetric distribution. Skewness greater than 0 indicates a positive bias ("positive tail") and skewness less than 0 indicates a negative bias ("negative tail"). |
|
Kurtosis |
Calculates the relative weight of central values to tail values in the sample distribution. The value is adjusted to a reference value of 0 for the Normal ("Gaussian") distribution. A kurtosis value greater than 0 indicates that the distribution is taller than a Normal distribution (too narrow, or "leptokurtic"). Conversely, a kurtosis value less than 0 indicates the distribution is flatter than a Normal distribution (too flat, or "platykurtic"). By definition, the Normal distribution has the reference ratio of central area to tail area adjusted to 0, and is called "mesokurtic". |
If an Image Set is open in the Image Window, you can choose whether to measure only the currently displayed member of the image set or compute the statistic for the entire image set. This is done using the Measure Image Set button in the Image Set Flags group on the Image Bar. When the button face shows a "1", then only the current (one) image is measured, otherwise, the entire image set is measured.
For Plot Windows, all Plot Series are measured.
Results of statistics measurements are tabulated in either a Statistics Measurements window used by all image windows or a private measurement pane owned by the Image Window or Plot Window. These hold the measurements in a Grid Control that includes menu commands for activities like sorting, rearranging, copying, saving, graphing, and opening in Microsoft Excel.
The first two examples below show statistics for an Image Window. The first example shows a Statistics Measurements window containing the Median value for members of an Image Set. The second example shows a measurement pane in which the Statistics Properties were changed to compare different estimators and parameters over the same rectangle in a single image.
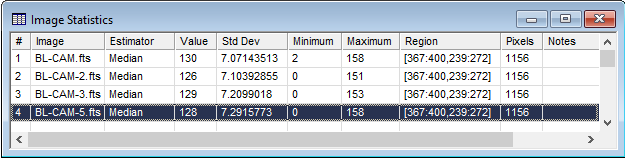
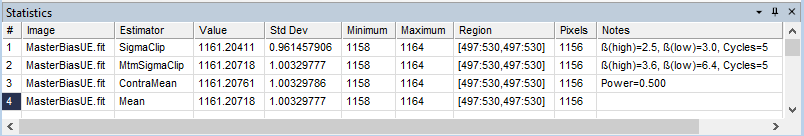
The picture below shows the Statistics window
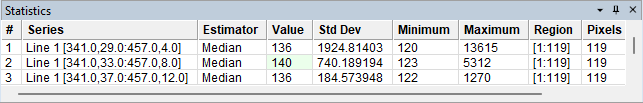
containing statistical estimators for the plot series in a Plot Window. Each line
corresponds to the calculation for a different Plot Series.
The Estimator listed in the table above
is chosen from the Statistics Properties window, then calculated using
the Measure > Statistics command
from the pull-down menu or the ![]() button on the
Image Measurements toolbar (Image Windows) or Plot Bar (Plot Window). One line
is added to the Statistics window for each plot series. You
can mark most results listed in the Statistics window on the
plot using the Mark
Statistics command of the Statistics window. Some
statistics cannot be marked, including the Standard Deviation, Standard
Error of the Mean, Skewness,
Kurtosis, Min, and Max.
button on the
Image Measurements toolbar (Image Windows) or Plot Bar (Plot Window). One line
is added to the Statistics window for each plot series. You
can mark most results listed in the Statistics window on the
plot using the Mark
Statistics command of the Statistics window. Some
statistics cannot be marked, including the Standard Deviation, Standard
Error of the Mean, Skewness,
Kurtosis, Min, and Max.
The Statistics window grid columns are described in the table below.
Statistics Report Grid Columns
|
# |
The sequence number of the measurement. |
|
Image |
For Image Windows, this is the name of the image. |
|
Series |
For Plot Windows, this is the title of the plot series. |
|
Estimator |
The name of the estimator used for the measurement. If the measurement has parameters (e.g., "SigmaClip"), then the parameters are listed in the Notes column. See Statistics Properties. |
|
Value |
The value of the estimator. See Statistics Properties. NOTE: Some estimators such as Standard Deviation calculate the standard deviation as the estimator; in these cases, the Value and Std Dev columns are identical. |
|
Std Dev |
The standard deviation from calculating the estimator. NOTE: Some measurements do not calculate the standard deviation (example: Minimum) and insert the value "0" as a placeholder in the table. In addition, the standard deviation and standard error calculations duplicate the estimator in the Std Dev column. |
|
Minimum |
The minimum value of the data sample. |
|
Maximum |
The maximum value of the data sample. |
|
Region |
Description of the pixel region that was measured. For images, the region uses the following format: [MinCol:MaxCol, MinRow:MaxRow] For plot series, there is only 1 row, so the format is [MinCol:MaxCol] |
|
Pixels |
The number of values sampled. |
|
Notes |
This column lists extra information such as the estimator parameters. However, the Notes cells may be edited to change this information or add other information. The Notes are included if you export the table to Excel or a file. |
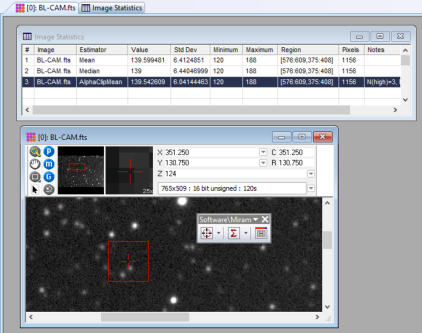
When making many measurements or repeatedly changing the Statistics Properties, it may be advantageous to detach the Measurements Toolbar from the Mira window border and move it over the Image Window or Plot Window, as shown below:
Mira Pro x64 User's Guide, Copyright Ⓒ 2023 Mirametrics, Inc. All
Rights Reserved.