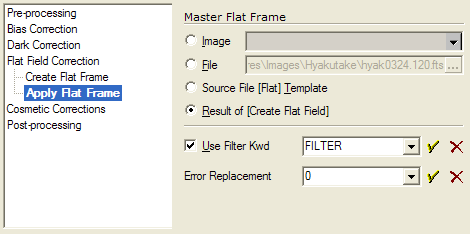
Apply Flat Frame
The Apply Flat Frame method is used by the Calibrate Images command to apply a flat field correction to images. This process is used to correct pixel to pixel sensitivity variations and/or illumination variations across the field of view. This process is used to correct pixel to pixel sensitivity variations and/or illumination variations across the field of view. To create master flat field frames from raw flat field frames, use the Create Flat Frame method or the Combine Images command.

Master Flat Frame Source
The Master Flat Frame may be loaded from a number of sources:
To use a displayed image, click the Image option and select an image from the Image Tree control. This selects one flat field frame for use by all target frames.
To load the master flat frame from a file, click the File option and specify the name of the file. This selects one flat field frame for use by all target frames.
To load from a source file using a template, such as 'flat*.fts', click the Source File [Flat] Template option and setup the template on the Flat page of the Source Files tab. If the Use Filter Kwd option is checked, then check this option to allow Mira to choose from among multiple master flats using the filter name.
To use the name assigned to master flat frame(s) created by the pipeline, click Result of [Create Flat Frame]. This option allows multiple flat field frames to be available for matching, if the Use Filter Kwd option is checked. Mira will then match the flat to the target image using the value of the specified filter keyword.
Requirements of the Master Flat Frame
The flat field correction is applied using an image known as a "Master Flat Frame". In actuality, a master flat frame is not an image showing a picture in the traditional sense, but is a map of pixel response as a function of position. To perform its function, the master flat frame must be correctly prepared from the raw flat field frames, and doing this requires attention to a number of critical details. If you allow the Image Calibration pipeline to create master flat(s) using the Create Flat Field method, and the present method uses the Result of [Create Flat Field] option, then the flat field correction will be correctly implemented. However, if you use the present method to load a pre-existing master flat, then you are responsible for it being properly prepared. Here are the requirements of a properly prepared master flat frame:
|
Bias Correction |
This correction must be applied unless it is automatically applied by the dark correction. Normally, the same correction procedure is used both for creating master flats and calibrating data frames. |
|
Dark Correction |
This correction must be applied unless the dark current is effectively 0. Normally, the same correction procedure is used both for creating master flats and calibrating data frames. |
|
Normalization to 1.0 |
The master flat must be scaled to a reference value of 1.0. Usually the reference region is the central 10 to 20% of the image. Normalization is necessary to create a map of pixel response to be applied to the data frames. To contain values normalized to 1.0 also means that a master flat must be saved with a real data type, such as 32 bit real or 64 bit real, so that the scaled values are correctly represented. |
|
Segregation by Filter |
A master flat frame must be created for the same filters as used to acquire the data frames. To apply the correction, Mira must be able to determine the filter used for the flats and the target data frames. Usually the FILTER keyword is used for this purpose in FITS format images. |
Matching Flat Frames by Filter Keyword
When a flat field frame is used to correct variations in pixel to pixel sensitivity, the flat frame must match the color of light to which the image was exposed. This means that a flat frame must be available for an image that was exposed through the same filter. If you specify a single file name, then there will be only 1 file that matches that name, which means that only one filter can be processed for a group of image on 1 run of this command.
Image Calibration can be made more efficient if more than 1 filter can be processed per run of this command. In addition, it is often useful to have filtered flat flat frames that have the same basic file name but differ by which filter they use. To meet both needs, Mira provides the file name Template option. If this item is selected, the flat frames are identified using the template and then the flat having the matching filter is applied to each image. To use this method, you need to set 3 preferences:
Click Template and specify a fie name pattern that will enable the flat frames to be located.
Click Use Filter Keyword.
Enter the name of the filter keyword.